Additives
Versatile and customizable, additives give you the range to do what you want with manufacturing
Welcome to Lintech, your go-to source for cutting-edge additives in the chemical industry. Additives refer to substances added to a product or material to enhance or modify its properties, performance, or processing characteristics. Additives aren’t the main components of the product but serve specific purposes to improve the overall quality or functionality. At Lintech, we understand the pivotal role additives play in optimizing performance, and our commitment is to bring you a diverse array of additives catering to a spectrum of needs.
Dive into our extensive product categories, where each additive serves a unique purpose. From ensuring stability and providing essential processing aids to infusing vibrant colors and pigmentation, we've got it all. Our additives go beyond the basics, venturing into realms of adhesion promotion, insulation, and anti-skinning. Discover the difference Lintech can make in elevating your chemical formulations to new heights – where innovation meets reliability.
Explore what additives can do for you
Experiencing defects in your formulations?
Making sure your formulation is perfect can be a long and strenuous process. We've seen it all, and below are some of the most common defects in formulation or application and the solutions we have found that provide the quality, durability, and aesthetics for an end product customers will love.
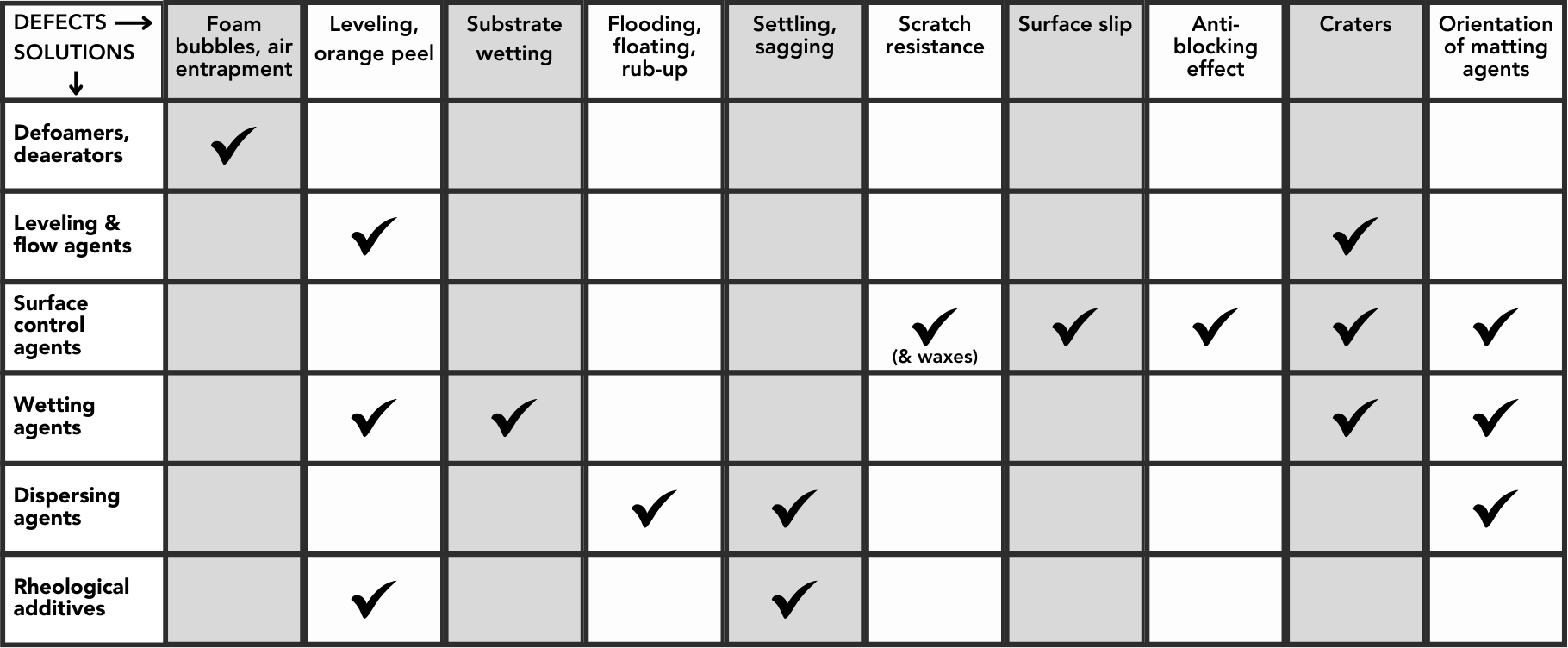
PRODUCT PORTFOLIO
Defoamers control and mitigate foam during various manufacturing processes. Foam, an undesirable accumulation of bubbles, can hinder process efficiency, disrupt the uniformity of coatings, paints, adhesives, and other formulations, and potentially lead to defects in the final product. Defoamers work by disrupting the foam stabilization process, either by promoting bubble coalescence or by reducing surface tension. Successful defoamers must meet specific requirements, including insolubility, low surface tension, positive penetration and spreading coefficients. Defoamers contribute to improved processing conditions, enhanced product quality, and overall operational efficiency by preventing or eliminating the challenges associated with unwanted foam.
- Defoamers (mineral oil-based, silicone-based, or polymer-based) to eliminate or prevent foam formation and enhance surface quality and prevent defects like pinholes and craters.
Flow and leveling agents are used in coatings and paints, where achieving a smooth and even surface is crucial. These agents enhance the fluidity of coatings during application, allowing them to spread uniformly over a substrate. Flow agents help to minimize surface defects such as brush marks, orange peel, or streaks by promoting a more controlled and consistent flow of the coating. Leveling agents contribute to the reduction of irregularities in the coating, ensuring an even film thickness. The combination of flow and leveling agents results in improved appearance, reduced surface tension, and enhanced overall performance of coatings, making them indispensable in various applications, including architectural coatings, industrial coatings, and specialty coatings for optimal aesthetic and functional outcomes.
- Flow & leveling additives (polyether-modified PDMS, silicone surfactant, and silicone- and fluoro-free organic polymer) to reduce the surface tension of the coating to improve flow and substrate wetting. Reducing surface tension helps to eliminate surface defects such as fisheyes and cratering.
- Non-ionic surfactants, ethoxylated alcohol, as substrate wetting agents.
Slip agents are designed to modify the surface properties of materials, providing a lubricating effect that reduces friction and enhances slipperiness. In coatings, slip agents contribute to the smoothness of the surface, preventing issues like blocking or sticking. They are especially valuable in applications where materials come into contact, such as coated paper or film. The incorporation of slip agents ensures ease of handling, prevents surface adhesion, and improves the overall performance of the final product. Whether in architectural coatings, industrial coatings, or specialty coatings, slip agents contribute to the tactile and functional qualities of the material, making them essential for achieving desired properties and enhancing the user experience.
- Fischer-Tropsch hard waxes for controlling open and set times, adjusting viscosity, and optimizing rheological behavior formulation while improving slip, scratch, and mar resistance.
- Surface modification additives for substrate wetting, leveling, anti-crater effects, and surface slip.
Wetting and dispersing agents are important for formulations involving pigments, dyes, and solid particles. These additives improve dispersion and stability of these solid components within liquid matrices. By reducing the surface tension between the particles and the liquid phase, wetting agents ensure efficient wetting of the solid surfaces, promoting uniform distribution. Dispersing agents work to prevent agglomeration or settling of particles, enhancing the overall homogeneity of the mixture. In applications like paints, coatings, and inks, achieving a consistent and stable dispersion of pigments is essential for product quality. Wetting and dispersing agents contribute to optimal formulation performance, ensuring that solid components are effectively incorporated, leading to improved color development, coating quality, and overall product characteristics.
- Compatibilizers to improve the compatibility between different components in a formulation, ensuring uniform mixing and stability
- Dispersing additives (polymeric and electrolytic) for stabilizing pigments and fillers, preventing flocculation, and optimizing color development. Designed for waterborne and solvent borne systems, they improve gloss, viscosity stability, and color uniformity across a variety of coatings and ink formulations.
- Ethoxylated alcohol non-ionic surfactants enhance wetting, stabilize dispersions, and improve pigment dispersion efficiency while being environmentally friendly and versatile across formulations.
- Multifunctional surfactants combine wetting, dispersing, and defoaming properties, improving pigment dispersion, reducing surface tension, and eliminating foam in formulations.
- Stearates, magnesium and zinc, for anti-caking to ensure a free-flowing consistency.
- Wetting agents (APEO-free, non-ionic, and polymeric) for improving the initial wetting of pigments, fillers, and substrates in coatings and inks. These additives reduce surface tension to enhance adhesion, promote color acceptance, and prevent defects like fisheyes and craters in both waterborne and solvent borne systems.
Rheological additives influence the flow and deformation characteristics of various formulations. They are designed to modify the rheological properties of fluids, affecting their viscosity, flow behavior, and overall mechanical response. In applications such as coatings, adhesives, and sealants, rheological additives help achieve desired consistency, application properties, and final product performance. They can enhance the stability of formulations, prevent sagging or dripping, and improve the ease of application and spreading. By tailoring the rheological behavior, these additives contribute to optimal product performance, ensuring that the material behaves as intended during processing, application, and throughout its functional life.
- Anti-settling additives prevent pigments, fillers, and other solids from settling during storage, ensuring uniform consistency and reducing the need for agitation.
- Rheology modifiers (HEUR-based thickeners and VOC-free and Stormer viscosity builders) to adjust the flow and viscosity of coatings to improve application properties, sag resistance, and stability. These modifiers are suitable for high-shear and low-VOC systems, ensuring consistent performance across various shear rates.
- Fischer-Tropsch hard waxes for controlling open and set times, adjusting viscosity, and optimizing rheological behavior formulation in plastics.
- Fumed silica, untreated/hydrophilic & surface-treated/hydrophobic, (KONASIL®) for viscosity & thixotropic control, preventing sag, and reducing clumping & caking.
- Kaolin clay for rheology control.
- Stearates, magnesium and zinc, for thickening formulations.
- Talc products that serve as cost-effective thixotropes and flatting pigments for architectural coatings providing sag and slump resistance, anti-setting properties, and viscosity stability.
Biological control additives and preservatives are designed to inhibit the growth and proliferation of unwanted microorganisms in formulations. In industries such as paints, coatings, and cosmetics, where water-based formulations are common, biological control additives help extend the shelf life of the product by suppressing the development of bacteria, fungi, and other harmful microbes. By incorporating these preservatives, formulators can enhance the overall quality and safety of their formulations, ensuring that end-users receive products with consistent performance and longevity. The use of these additives aligns with industry standards for quality assurance and regulatory compliance, promoting the production of high-quality chemical products across diverse applications.
- Additives for microbial control for dry film and in can preservation for use in architectural, industrial, and specialty coatings.
Matting agents are used to control and adjust the gloss or shine of coatings, paints, and other formulations. These additives work by creating a microscopically rough surface on the coated material, scattering light and reducing its reflective properties which results in a matte or satin appearance. Matting agents are commonly used in applications such as paints, varnishes, and printing inks to achieve the desired level of sheen, enhance texture, and improve overall visual appeal. The selection of matting agents depends on the specific formulation requirements, and these additives contribute significantly to the versatility and customization of coatings across various industries.
- Calcined clays are specifically designed to lower TiO2 levels, control sheen for maximum matte effect, and improve tint strength, touch-up, and scrub & burnish resistance.
- Diatomaceous earth (DE) can be used as paint pigment extender and flatting agent in paints and coatings.
- Fischer-Tropsch hard waxes as matting agents for control over gloss.
- Precipitated silica for coatings, paints, and varnishes to impart a matte finish to surfaces.
- Talc products can serve as cost-effective thixotropes and flatting pigments for architectural and industrial coatings providing sag and slump resistance, anti-setting properties, and viscosity stability.
Plasticizers are incorporated into plastics, rubbers, and other polymeric substances to modify their physical properties, making them more flexible, workable, and durable. Plasticizers work by reducing the intermolecular forces within the polymer matrix, allowing for increased mobility between polymer chains. This imparts greater malleability, improved elongation, and enhanced resistance to cracking or brittleness. Commonly used in the production of PVC, elastomers, and various polymer blends, plasticizers contribute to the versatility and functionality of a wide range of end products, including flexible films, coatings, and molded items in industries such as construction, automotive, and packaging.
- Plasticizers for viscosity modifiers and plasticizing effects.
Flash rusting is an immediate and undesirable oxidation that can occur on metal surfaces before a protective coating fully cures or dries. Flash rust inhibitors function by forming a protective barrier on the metal substrate, inhibiting the corrosive effects of moisture and atmospheric conditions. These inhibitors are used in applications such as paint and coating formulations for metals to ensure the longevity, appearance, and performance of the coated metal surfaces. By mitigating the risk of early-stage rusting, flash rust inhibitors contribute to the overall effectiveness and durability of coatings, providing long-lasting protection to metal structures and products.
- Flash rust and anti-corrosion additives provide in-can rust protection and improve corrosion resistance of paint films.
- HeucoflashTM products are a solution of organic and inorganic compounds and salts for flash rust inhibition. These products are VOC free and are commonly used in combination with anti-corrosive pigments.
Catalysts act as initiators or accelerators in chemical reactions, facilitating the conversion of reactants into desired products. In polymeric systems, catalysts play a crucial role in polymerization reactions, enabling the creation of polymers with specific properties. Whether it's promoting curing reactions in adhesives, accelerating chemical transformations in the synthesis of specialty chemicals, or ensuring efficient cross-linking in resin systems, both driers and catalysts are indispensable for controlling the pace and outcome of chemical processes in the industry.
- Driers to accelerate the drying process in alkyd-based paints, coatings, and inks. Primary driers initiate surface drying, secondary driers enhance through drying, and auxiliary driers modify overall drying efficiency.
- Cobalt-free driers for environmentally friendly and regulatory-compliant formulations, delivering efficient surface and through drying without the color or toxicity issues of cobalt. Suitable for alkyd paints, urethane coatings, and inks, offering comparable performance with a sustainable edge.
- Combination driers, pre-formulated blends of primary and secondary driers, for balanced drying performance, prevent gelling during storage, and offer tailored solutions such as lead- and cobalt-free options to meet regulatory and environmental requirements.
- Loss-of-dry inhibitors inhibit drying inefficiencies caused by pigment absorption or water interactions, maintaining long-term storage stability.
- Metal carboxylates (including metal-based driers like cobalt, manganese, zirconium, calcium, barium) act as drying agents in alkyd-based systems, facilitating oxidative polymerization for surface and through drying.
- Tin-based and tin-free catalysts used for specific end-use industries such as PVC, polyurethanes, and composites. These catalysts are designed for precise control in curing and reaction processes.
Specialty additives address specific challenges or enhance particular characteristics in end products. From advanced polymers to coatings, specialty additives play a crucial role in achieving desired outcomes such as improved performance, enhanced durability, or unique functionalities. Examples include additives for UV stabilization, adhesion promotion, conductivity, and insulation, each serving a specialized purpose within specific applications. The versatility and specificity of specialty additives make them valuable tools for formulators and manufacturers aiming to meet precise requirements and deliver innovative solutions in a wide array of industries.
- Anti-skinning agents to prevent skin formation in paint cans, ensuring consistent application without hindering surface drying. Multiple products and chemistries for flexibility in meeting regulatory requirements for in-can skin formation in alkyd coatings.
- Coalescing agents (low-VOC, biobased options) to enhance film formation and reduce VOC content in solventborne alkyds.
- Diatomaceous earth (DE) can be used as an anti-blocking agent in the production of clear polyethylene and polypropylene films.
- Hollow ceramic microspheres with high temperature resistance (MP > 1800 °C) for thermal insulation, compressive resistance, and acoustic insulation.
- Fischer-Tropsch hard waxes for anti-blocking agents in coatings.
- Silanes (amino, multifunctional, water-based) for adhesion promotion.
- Stearates, magnesium and zinc, can be used as release agents during the production of molded goods, lubricants during plastics manufacturing, and waterproofing agents for coatings.
- UPR (unsaturated polyester resin) putty additives for reducing viscosity, enhancing filler dispersion, and preventing settling in unsaturated polyester and epoxy resin systems. These also include air-releasing agents to eliminate entrapped air during application, improving finish quality.
About Us
Founded in 1983 in Macon, GA, Lintech has evolved into a leading distributor, showcasing remarkable adaptability and consistent growth over its 40-year journey. Lintech is a privately owned company united by a shared purpose. We cultivate a dynamic and spirited team, united in our dedication to reaching shared goals. Lintech's mission is anchored in the pursuit of excellence. In partnership with our suppliers, we are committed to providing unparalleled service to our valued customers. As a nimble and independent distributor, we bring a personalized touch to your needs, ensuring agility and responsiveness. Choosing Lintech means choosing a dedicated partner committed to delivering the highest quality products and creative solutions for the diverse challenges within the chemical industry. Come explore our certifications and embark with us on a journey toward innovation and success, where reliability and collaboration define our path forward.

.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Additives%201140px%20x%20850px%20(6).png)

.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Additives%201140px%20x%20850px%20(2).png)
.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Additives%201140px%20x%20850px%20(5).png)
.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Additives%201140px%20x%20850px%20(3).png)
.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Additives%201140px%20x%20850px%20(4).png)


